A. Overview of Weight Loss Surgeries
Weight loss surgeries, also referred to as bariatric surgeries, encompass a range of medical procedures aimed at aiding individuals in losing weight and managing obesity-related health issues. These surgeries alter the digestive system’s anatomy to restrict food intake, promote satiety, and sometimes reduce the absorption of nutrients. In recent years, the prevalence of obesity has risen significantly, prompting more individuals to explore surgical options for weight loss.
B. Significance of 20,000 Americans Opting for Weight Loss Surgeries in 2024
In 2024, a noteworthy trend emerged as 20,000 Americans chose weight loss surgeries as a means to address their obesity concerns. This statistic underscores a shifting perspective towards bariatric interventions and highlights the growing acceptance of surgical solutions in combating obesity. The decision of these individuals reflects a desire for improved health and quality of life, driving them to pursue transformative surgical procedures.
C. Purpose of the Article
This article endeavors to delve into the multifaceted landscape of weight loss surgeries, examining their various types, the factors driving their increased adoption, their impact on health and well-being, as well as the challenges and considerations associated with them. By providing a comprehensive exploration of this topic, the aim is to empower readers with knowledge and insights to make informed decisions regarding weight loss interventions.
Types of Weight Loss Surgeries
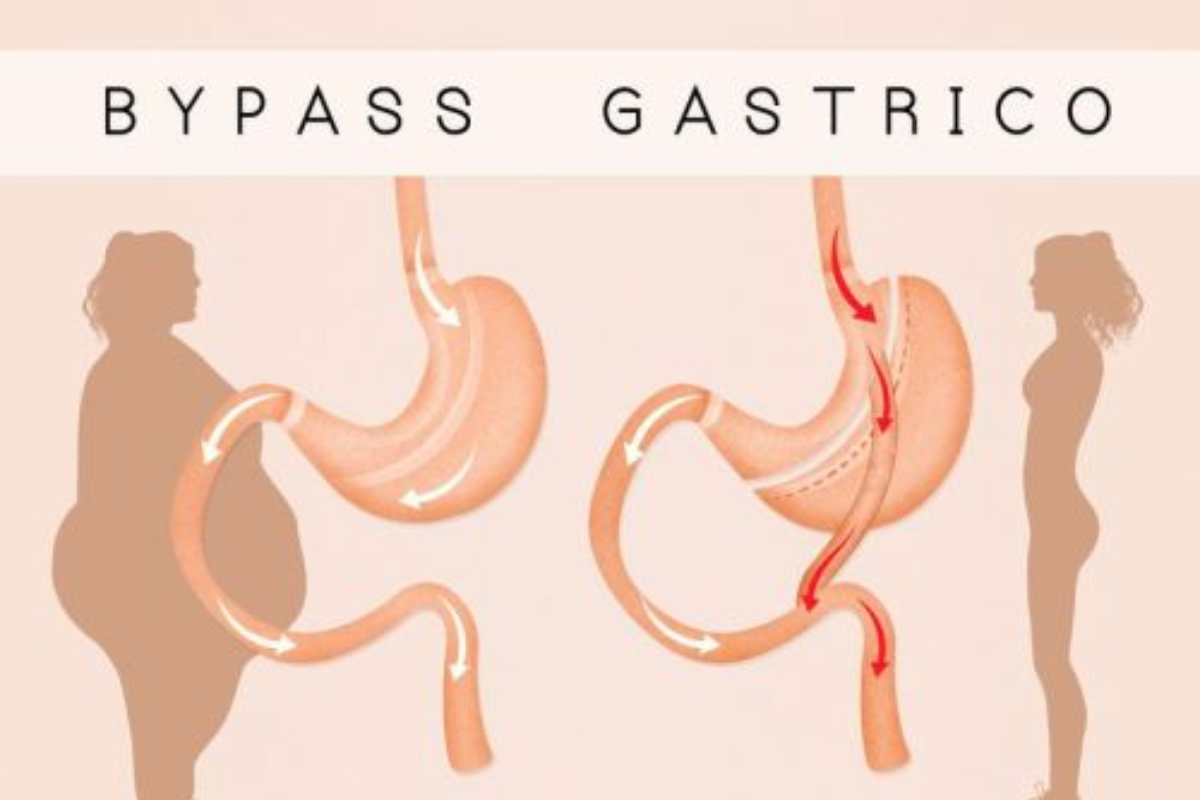
A. Gastric Bypass Surgery
Gastric bypass surgery stands as one of the most prevalent and effective weight loss procedures available. The surgery involves creating a small stomach pouch and rerouting the digestive tract to bypass a portion of the small intestine. This results in both restrictive and malabsorptive effects, significantly reducing the amount of food that can be consumed and absorbed. Gastric bypass surgery often leads to substantial weight loss and improvement in obesity-related comorbidities such as type 2 diabetes and hypertension.
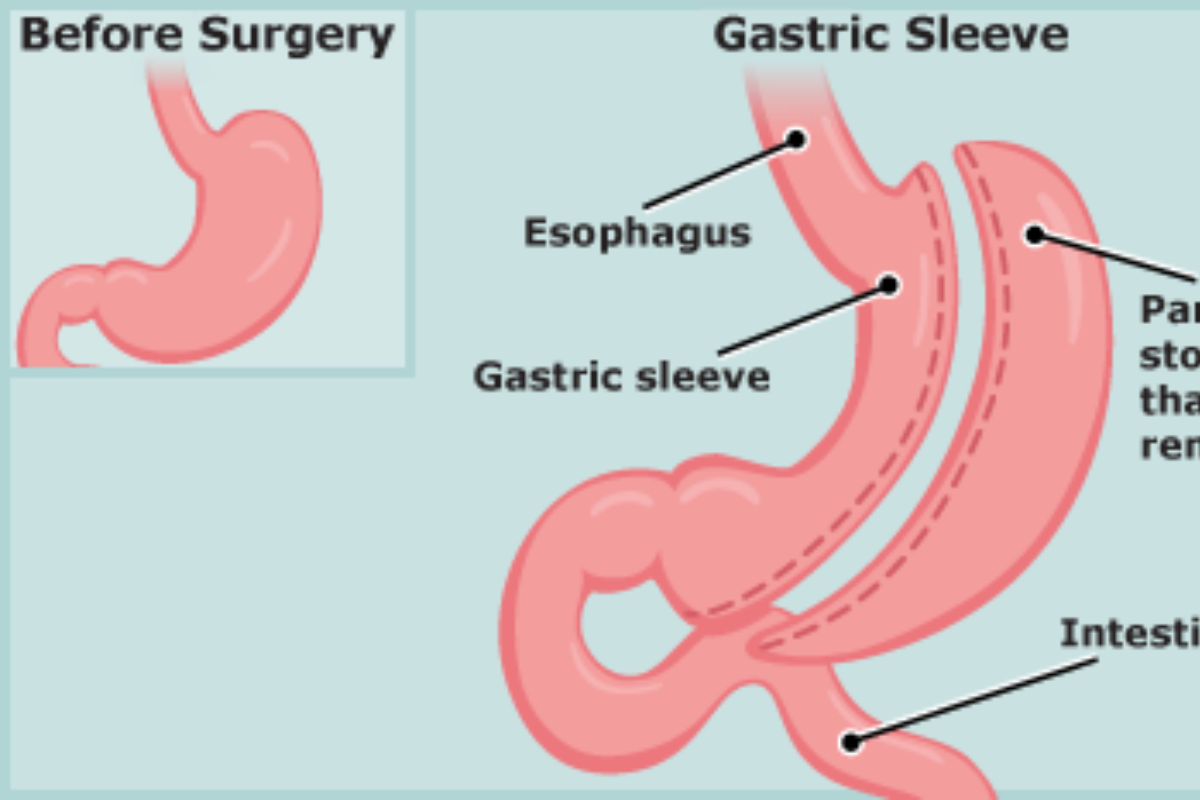
B. Gastric Sleeve Surgery
Gastric sleeve surgery, also known as sleeve gastrectomy, involves the removal of a large portion of the stomach, leaving a slender tube or “sleeve.” This procedure restricts the amount of food that can be consumed while preserving the natural continuity of the digestive tract. Gastric sleeve surgery is less complex than gastric bypass and carries a lower risk of complications. It has gained popularity due to its effectiveness in promoting weight loss and its relatively straightforward surgical approach.
C. Laparoscopic Adjustable Gastric Banding (LAGB)
Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding (LAGB) entails placing an inflatable band around the upper part of the stomach, dividing it into a smaller upper pouch and a larger lower pouch. The band can be adjusted to regulate the size of the passage between the two pouches, controlling the amount of food intake. LAGB is a reversible procedure and does not involve stomach stapling or intestinal rerouting. While it offers a less invasive option for weight loss, it may require frequent adjustments and has a lower long-term success rate compared to other bariatric surgeries.
D. Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch (BPD/DS)
Biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch (BPD/DS) is a complex procedure that combines restrictive and malabsorptive elements. It involves removing a portion of the stomach to create a smaller stomach pouch and rerouting the intestines to limit the absorption of calories and nutrients. BPD/DS results in significant weight loss and improvement in metabolic conditions but carries a higher risk of nutritional deficiencies. It is typically reserved for individuals with severe obesity or those with significant obesity-related health issues.
Reasons Behind the Surge in Weight Loss Surgeries
A. Increasing Obesity Rates in the United States
The rising prevalence of obesity in the United States has contributed significantly to the surge in weight loss surgeries. Despite extensive efforts to combat obesity through lifestyle modifications and medical interventions, many individuals continue to struggle with excessive weight gain. With obesity being a major risk factor for various chronic diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, and certain cancers, more individuals are turning to surgical solutions to address their weight-related health concerns.
B. Improved Accessibility and Acceptance of Weight Loss Surgeries
Advancements in medical technology and greater accessibility to weight loss surgeries have played a pivotal role in their increased acceptance. Over the years, bariatric procedures have become safer, more effective, and more widely available. Additionally, the growing body of evidence supporting the long-term benefits of weight loss surgeries has led to increased acceptance among healthcare professionals and patients alike. As a result, more individuals are opting for these procedures as a viable solution for achieving sustainable weight loss and improving their overall health.
C. Medical Advancements and Safety of Procedures
Advancements in surgical techniques and perioperative care have significantly enhanced the safety and efficacy of weight loss surgeries. Minimally invasive approaches such as laparoscopic and robotic-assisted surgeries have reduced surgical risks, postoperative pain, and recovery time, making these procedures more appealing to patients. Furthermore, comprehensive preoperative assessments and multidisciplinary care teams ensure that patients are thoroughly evaluated and supported throughout their surgical journey, further minimizing complications and optimizing outcomes. As a result, individuals are increasingly confident in the safety and effectiveness of weight loss surgeries, leading to a surge in their utilization.
Impact of Weight Loss Surgeries on Health and Quality of Life
A. Physical Health Benefits
Weight loss surgeries offer a myriad of physical health benefits that extend beyond mere weight reduction. Significant weight loss following these procedures can lead to improvements in obesity-related comorbidities such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and obstructive sleep apnea. Moreover, bariatric surgeries have been shown to reduce the risk of cardiovascular events and mortality in obese individuals. By achieving sustainable weight loss and effectively managing obesity-related health conditions, patients experience enhanced physical well-being and a higher quality of life.
B. Psychological Effects and Mental Well-being
In addition to their physiological impact, weight loss surgeries can profoundly influence psychological well-being and mental health. Many individuals who undergo these procedures report improvements in self-esteem, body image, and overall psychological functioning. By shedding excess weight and achieving their desired body shape, patients often experience increased confidence and a greater sense of control over their lives. Furthermore, the resolution of obesity-related psychological issues such as depression and anxiety contributes to enhanced mental well-being and overall life satisfaction.
C. Lifestyle Changes and Long-term Success
Weight loss surgeries serve as a catalyst for lifestyle modifications that are essential for long-term success. Patients are required to adhere to strict dietary guidelines, engage in regular physical activity, and attend follow-up appointments to optimize outcomes and prevent weight regain. These lifestyle changes not only facilitate sustained weight loss but also promote overall health and wellness. By adopting healthier habits and behaviors, patients can enjoy the long-term benefits of weight loss surgeries and maintain their results for years to come.
Challenges and Considerations
A. Potential Risks and Complications
Despite their effectiveness, weight loss surgeries are not without risks and complications. Surgical complications such as infection, bleeding, and leakage at the surgical site can occur, albeit rarely. Additionally, some patients may experience adverse reactions to anesthesia or develop blood clots postoperatively. Long-term complications such as nutrient deficiencies, gallstones, and gastrointestinal issues may also arise. It is essential for patients to be aware of these potential risks and work closely with their healthcare team to minimize them.
B. Pre-operative and Post-operative Care
Comprehensive pre-operative evaluation and preparation are crucial for ensuring the safety and success of weight loss surgeries. Patients undergo thorough medical assessments, including evaluations of their overall health, nutritional status, and psychological well-being. Additionally, they receive counseling on the anticipated lifestyle changes and commitments required postoperatively. Following surgery, patients require ongoing post-operative care and support to monitor their progress, manage any complications, and adjust to their new dietary and exercise regimens.
C. Lifestyle Modifications and Dietary Changes
Successful outcomes following weight loss surgeries hinge on sustained lifestyle modifications and dietary changes. Patients must adhere to a modified diet consisting of small, nutrient-dense meals to accommodate their altered anatomy and promote weight loss. Moreover, regular physical activity is essential for maintaining muscle mass, preventing weight regain, and improving overall health. Adopting these lifestyle changes can be challenging and may require ongoing support from healthcare professionals, dietitians, and support groups to ensure long-term success.
Societal Implications and Future Trends
A. Economic Factors and Healthcare Costs
The economic implications of weight loss surgeries extend beyond individual patients to encompass healthcare systems and society as a whole. While these procedures can result in substantial cost savings by reducing the burden of obesity-related healthcare expenditures, they also incur significant upfront expenses. Access to weight loss surgeries may be limited by financial barriers, insurance coverage limitations, and disparities in healthcare access. As such, addressing these economic factors is crucial for ensuring equitable access to bariatric interventions and mitigating the long-term societal costs of obesity.
B. Cultural Attitudes towards Obesity and Weight Loss Surgeries
Cultural attitudes towards obesity and weight loss surgeries play a significant role in shaping individuals’ perceptions and decisions regarding these procedures. While there has been growing acceptance and normalization of bariatric surgeries in recent years, stigma and misconceptions surrounding obesity persist in many societies. Addressing these cultural barriers requires comprehensive education, advocacy, and destigmatization efforts to promote understanding, empathy, and support for individuals struggling with obesity.
C. Predictions for the Future of Weight Loss Surgeries
The future of weight loss surgeries is characterized by continued innovation in surgical techniques, patient selection criteria, and perioperative care strategies. Minimally invasive approaches, such as robotic-assisted and endoscopic procedures, are likely to become more widespread, further reducing surgical risks and enhancing patient outcomes. Additionally, personalized medicine approaches, including genetic profiling and metabolic testing, may enable tailored interventions to optimize individual responses to bariatric surgeries. Furthermore, advancements in telemedicine and digital health technologies offer new opportunities for remote monitoring, patient support, and follow-up care, enhancing the accessibility and effectiveness of weight loss interventions.
Common Questions About Weight Loss Surgeries
Q1. What are weight loss surgeries, and how do they work?
A: Weight loss surgeries, also known as bariatric surgeries, are medical procedures designed to help individuals lose weight by altering the anatomy of the digestive system. These surgeries work through various mechanisms, including restricting the amount of food that can be consumed, reducing the absorption of nutrients, or a combination of both.
Q2. Who is a candidate for weight loss surgery?
A: Candidates for weight loss surgery typically include individuals who have been unsuccessful with traditional weight loss methods such as diet and exercise and have a body mass index (BMI) of 40 or higher (or a BMI of 35 or higher with obesity-related health issues such as type 2 diabetes or hypertension). However, eligibility criteria may vary depending on individual health factors and surgical guidelines.
Q3. What are the different types of weight loss surgeries available?
A: The most common types of weight loss surgeries include gastric bypass surgery, gastric sleeve surgery, laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding (LAGB), and biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch (BPD/DS). Each procedure works through different mechanisms to achieve weight loss and may be recommended based on individual health needs and preferences.
Q4. What are the risks and complications associated with weight loss surgeries?
A: While weight loss surgeries are generally safe and effective, they do carry risks and potential complications. These may include surgical risks such as infection, bleeding, and leakage, as well as long-term complications such as nutrient deficiencies, gallstones, and gastrointestinal issues. It’s essential for individuals considering these procedures to discuss potential risks with their healthcare provider.
Q5. What is the recovery process like after weight loss surgery?
A: The recovery process following weight loss surgery varies depending on the type of procedure performed and individual factors. In general, patients can expect to stay in the hospital for a few days after surgery and gradually resume normal activities over several weeks. Following discharge, patients will be advised to follow a modified diet and exercise plan and attend regular follow-up appointments to monitor their progress and address any concerns.
Q6. Will I need to make lifestyle changes after weight loss surgery?
A: Yes, lifestyle changes are an essential component of long-term success following weight loss surgery. Patients will be required to adhere to a modified diet consisting of small, nutrient-dense meals, engage in regular physical activity, and attend follow-up appointments with their healthcare provider. These lifestyle modifications are crucial for achieving and maintaining weight loss, improving overall health, and preventing weight regain.
Q7. What results can I expect from weight loss surgery?
A: Weight loss surgery can lead to significant and sustained weight loss, as well as improvements in obesity-related health issues such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and obstructive sleep apnea. Many patients also experience improvements in quality of life, self-esteem, and overall well-being. However, individual results may vary, and it’s essential to have realistic expectations and commit to long-term lifestyle changes for optimal outcomes.

